All data has value, but not the same value. Critical data needs to be accessible while sensitive data needs stringent controls and less important data needs less resources. When DLP is adapted to specific data priorities and context and baked into workflows, rather than bolted on, compliance is easier and part of everyday operations.
Below is an analysis of data loss prevention (DLP), its relevance in the contemporary data-driven world, the risks it mitigates, the regulatory compliance it meets, and the steps for implementing it successfully.
The following challenges, strategies, and implementation essentials can help any organization take a practical, effective, and collaborative approach to data loss prevention.
What is DLP?
Data loss prevention helps protect high-value, high-risk data using a montage of processes and tools. Data is at the core of most business operations, and the more reliant a business is on data, the more important DLP becomes.
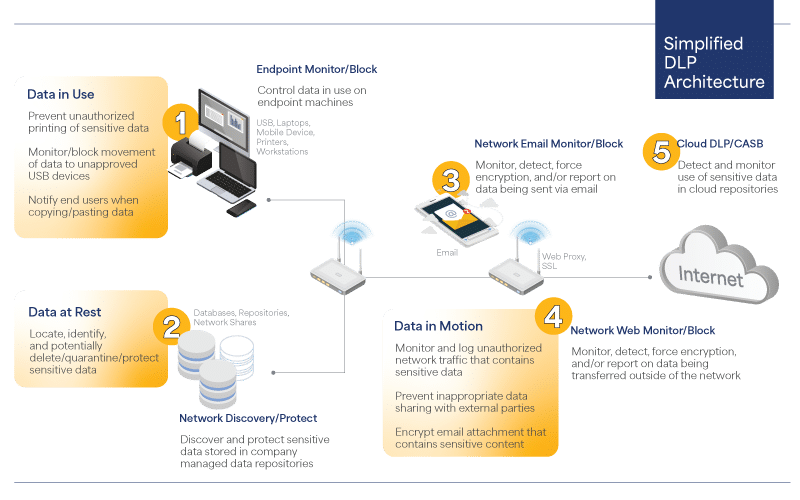
A DLP strategy focuses on protecting the most important data from loss, misuse, and access by unauthorized users. DLP solutions support that strategy by tracking and protecting the organization’s data at rest, in motion, and in use.
Why data loss protection matters
Data is a shared commodity, passing between businesses and consumers with nearly every interaction. When data is lost, the breached organization is only one victim among many possible others. Consider when a bank is breached. Even when not directly the target, its customers can face severe, long-term financial impact and loss of personally identifiable information (PII). Its vendors and business partners face unknown fallout and heightened risk of a data breach.
Depending on the industry and geographical location, data protection rules and regulations are in place to ensure that using, collecting, or storing data integrates security and privacy best practices. An artfully crafted DLP strategy meets those applicable compliance requirements and reduces the risk of a data breach.
Four reasons that make DLP a strong component of modern data management
- Risk mitigation
Preventing unauthorized access and inadvertent sharing of sensitive data significantly reduces the risk of a data breach. Internal breaches are rising and now count for 28% of all breaches. An internal user attempting to send confidential data to someone not authorized for access, whether accidentally or intentionally, is blocked by the DLP solution and security incident response team is alerted. - Compliance assurance
DLP helps meet data security and privacy regulations by ensuring proper handling and protection.- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) gives California residents the right to know how their personal data is used, shared, and stored. DLP solutions monitor how data is used, transferred, or stored, and prevents misuse.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates the protection of personal data and privacy of EU citizens. DLP solutions prevent unauthorized access and transfer of this data, ensuring compliance.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires the protection of sensitive patient health care information. Preventing the sharing of unencrypted data is one way that a DLP solution supports HIPAA compliance.
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) applies to merchants and payment processors and requires the protection of cardholder data to protect users, prevent fraud, and ensure the integrity of the payment card industry. DLP solutions help meet PCI DSS requirements by monitoring the use and transfer of cardholder data.
- Trust and reputation
When a data leak occurs, customer trust and brand reputation are eroded. Reclaiming or rebuilding what is lost can take years, especially when customers and potential customers are easily reminded of the breach whenever doing online research. DLP plays a role in ensuring brand integrity and competitive well-being by helping to prevent data loss incidents and keeping organizations out of the news. - Avoiding penalties
Organizations that are non-compliant with industry, federal, and state regulations face severe financial penalties. In the case of GDPR, any company that fails to meet the guidelines faces a fine as high as 4% of annual global revenue from the previous year.
Breaking through DLP implementation challenges
DLP in the abstract is one thing. In reality, implementing an effective DLP strategy means balancing data protection, business objectives, and user needs.
Data classification
Challenge: Critical and sensitive data, such as PII and cardholder data, must be identified and categorized appropriately to avoid exposure, risk, and wasted resources. Incorrectly applying DLP to all data is intensive, expensive, and ineffective.
Solution: Use data classification to label all data used in each area of the organization. The most common classification levels are public, internal, confidential, and restricted. Once done, it’s much easier to identify data value and where it fits into the DLP strategy.
False positives
Challenge: When DLP policies are too restrictive, it can lead to an overload of false positives. This strains operations, leads to alert indifference, and could cause a true issue to be overlooked. Overly restrictive DLP policies can inadvertently undermine security and compliance by crying wolf too often. However, policies that aren’t restrictive enough also carry risks by not detecting potential data leakage.
Solution: The ideal balance is reasonable restriction while enabling business activity – not too much, not too little. Use a continuous review/improve flow to fine-tune policies. It’s a journey, not a one-and-done effort.
- Policies should be as specific as possible. Consider defining more granular rules based on data type, use context, and location.
- Deploy policies over time. Start with a few rules and add more as impact is interpreted. Make adjustments as needed. DLP performance will gradually be more sophisticated as control over false positives improves.
- Data classification also helps reduce false positives, making it a dual performer in the rollout and continued improvement of DLP.
- Implement user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to understand normal behavior patterns in systems. UEBA solutions use machine learning (ML) algorithms to establish patterns to identify anomalies and potential threats, helping lower the rate of false positives.
- Track the rate of false positives. Increases likely mean it’s time to review and update your DLP rules to reflect the evolving data environment and threat landscape. Choose a DLP solution with advanced detection technique capabilities, such as fingerprinting, watermarking, and ML to improve data detection accuracy.
Cultural change
Challenge: Some people resist even small changes. Changing how someone interacts with the data used daily for their job is a big change. Resistance, concerns about loss of productivity, and perceptions of interference are likely.
Solution: Before implementing DLP, help employees understand why it’s being implemented, how it will be implemented, and how it safeguards customers, employees, and the organization from the economic blows of a data breach. Continue those sessions routinely to bring new employees into the program, reinforce good data hygiene with existing employees, and to update everyone on any changes affecting them.
The art of DLP implementation
With potential roadblocks acknowledged and addressed, use the following steps to guide a successful DLP implementation.
- Understand business processes: Before implementing a DLP solution, it’s crucial to have a thorough understanding of the organization’s business processes. This understanding informs what data is collected, how and where it is stored, how it is shared, and who has access to it. This step is vital for identifying potential data loss risks associated with each process. For example, a process that involves sharing customer data with third-party vendors would need robust controls to prevent data leakage.
- Identify key stakeholders throughout the organization: DLP impacts every department, function, and user. Including the right people in the process can make all the difference in adoption and success. Consider including these roles or representatives from these areas:
- Senior management: Top-down support and approval for resources are necessary for success.
- Information security: This group will be instrumental in defining DLP policies, overseeing implementation, and monitoring the program.
- Business information security officer: This role is a liaison between business area owners and the information security team. They help build policies with an understanding of the business processes around data.
- Legal: Get it right, right from the beginning by ensuring that the DLP program meets all legal and regulatory requirements.
- IT: Engage early in project development so that meeting technical needs, challenges, and implementations are in alignment with the desired rollout.
- Compliance: Since this is a DLP adoption driver, meeting compliance requirements is essential to meeting objectives.
- Accounting, customer service, marketing, sales, and others: While not integral to the project, each business area must identify and classify its data sets and associated functions. Buy-in in these areas helps support broader acceptance.
- End users: While they won’t make or break the project, they can affect whether implementation is bumpy or smooth. Frequent communication, updates, and training go a long way with this group.
- Define objectives: Identify program’s key goals, which could include meeting compliance requirements and protecting intellectual property.
- Identify sensitive data: Use data discovery and classification to identify the data requiring protection, including PII, cardholder data, and other valuable data.
- Select a DLP solution: Due diligence in researching available vendor solutions, offered features and capabilities, and integration with existing systems will produce the best solution for the organization’s specific needs and requirements. Not sure what to look for? The top traits of a great DLP are listed below.
- Hire a dedicated team: With a skilled team in place, the DLP solution can be appropriately configured, optimized, and integrated into the environment, and resources will be available to sustain the processes and support the business.
- Implement the DLP solution: Deploy across the organization and integrate with other systems, which may include installing DLP software on all servers and employee devices.
- Develop policies: Base policies on identified objectives, business requirements, data types, and regulatory requirements.
Example policy
An organization with an accepted business practice of sharing customer PII with an approved third-party vendor through encrypted email but stipulations prohibiting printing of that information could implement these DLP policies:- Endpoint DLP policy to prevent printing
- Email DLP policy to block sending the data unencrypted to the authorized recipient
- Email DLP policy preventing data from being emailed to any unauthorized addresses
- Develop processes and workflows: As processes are developed and refined, create documentation that supports continued management of the DLP solution.
- Monitor and respond: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of the DLP program and make necessary adjustments. Re-calibration is essential as the environment, data, and risks evolve.
Key capabilities of top-performing DLP solutions
What should you look for in DLP technology? The following characteristics provide wide-ranging performance to align with requirements
- Comprehensive data coverage: Data in motion, at rest, and in use should be covered. This includes the ability to monitor emails, web uploads, file transfers, and user actions on devices.
- Advanced data detection techniques: Capabilities like fingerprinting, exact data matching, image recognition—such as OCR—and machine learning help detect sensitive data accurately. Using exact data as a reference helps identify and match for access and transmission to reduce false positives, rather than relying on a simple number pattern or regular expression (RegEx). Using ML can identify patterns in data access and usage that suggest a data breach.
- Scalability: The solution should be able to handle the volume of data in large organizations and scale as the organization grows.
- Integration capabilities: Look for easy integration into existing systems, such as security information and event management systems (SIEMs), identity and access management (IAM) solutions, mail transfer agents (MTAs), and secure web gateways.
- Reporting and analytics: Detailed reports and analytics should provide insights into potential risks and the effectiveness of the DLP program.
Data loss prevention is elemental
Modern data protection weaves together essentials that safeguard data from loss, damage, and threats. DLP is a primary component, offering protection against data breaches and regulatory non-compliance.
Fusing this information with a structured, strategic approach puts everything necessary in place for a holistic, successful DLP implementation. Converge offers guidance, professional services, and solutions delivered by skilled data experts for any stage of DLP. Reach out today to learn more.